This work is currently under peer review
Smartphones are increasingly used for monitoring road roughness conditions. However, the smartphone-based roughness index estimation system (sRIE) is vulnerable to variations in vehicle type, driving speed, and mounting configuration. Among these factors, mounting has been underexplored, despite its significant influence on the smartphone-collected vehicle response data. This study aims to quantify the effects of four typical mountings on smartphone-collected response data and develop a method to correct their signals to accurately reflect the vehicle-body response. An empirical-based correction function was obtained from a laboratory vibration test and validated using real-world vehicle response data. This study found that the mountings amplify the signals in a 6 - 18 Hz frequency band, depending on their arm length and rigidity, while attenuating the amplitudes of vibrations above 30 Hz. The proposed method reduces the differences caused by different mountings through amplitude correction in frequency bands. This study provides insights into mounting’s effect on sRIE and contributes to crowdsourcing-based pavement roughness monitoring.
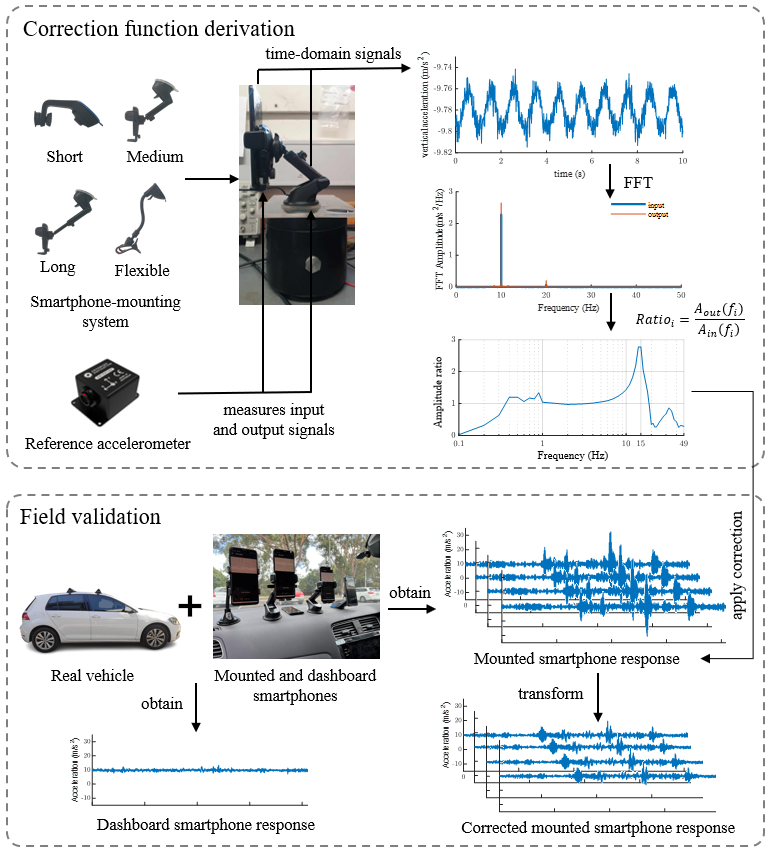
As shown in the schematic plot below, in the first step, the smartphone-mounting configurations were isolated and tested using a laboratory vibration table. Sinusoidal vibrations were applied to the smartphone mounting system, and the response data at input and output locations was collected by the accelerometer. Then, the response data is transformed into the frequency domain, and the amplitude value of both the input and output is used to plot the frequency response spectrum, and an empirical-based correction function is obtained. This step learns the mounting’s amplification or attenuation pattern across the frequency spectrum. This correction function adjusts the mounted smartphone-collected signals so that they reflect the vehicle body response more accurately. Last, the correction functions were validated in a real-world roughness data collection context. This step ensures that the proposed correction method is effective in real-world applications
Research framework
Mounting vibration test